Ant Queens | Understanding Ant Queens: Colony Founders
Ants are prolific insects, with over 12,000 identified species worldwide. They can form colonies ranging from a few individuals to supercolonies spanning thousands of kilometers. Ant colonies are made up of several castes, including workers, soldiers, and of course, the queen.
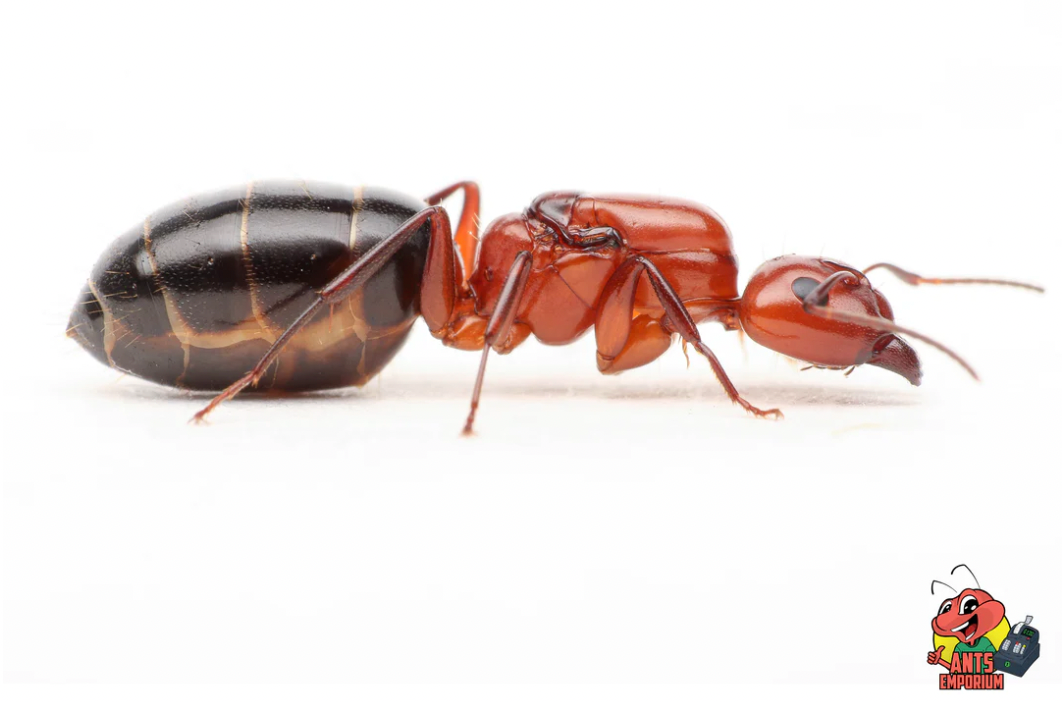
The queen's role is to lay eggs, thus continuing the colony's existence. Her position gives her significant power within the colony, and she serves as the heart of the social structure that keeps the colony thriving. Understanding the significance of ant queens is key to understanding the behavior and survival of the colony as a whole.

Key Takeaways
- Ant queens play a vital role in ant colonies' social structure, serving as the leaders and founders.
- The queen's primary role is to lay eggs, ensuring the continuity of the colony.
- Ant colonies have a complex social structure, with different castes serving specific roles.
- The queen's position within the colony grants her significant power to shape the colony's behavior and organization.
- Understanding ant queens is fundamental to understanding the behavior and survival of ant colonies.
The Life of an Ant Queen
Ant queens are undoubtedly some of the most important members of the ant colony. Their life cycle is quite fascinating, and understanding it is crucial to understanding the workings of the colony as a whole.
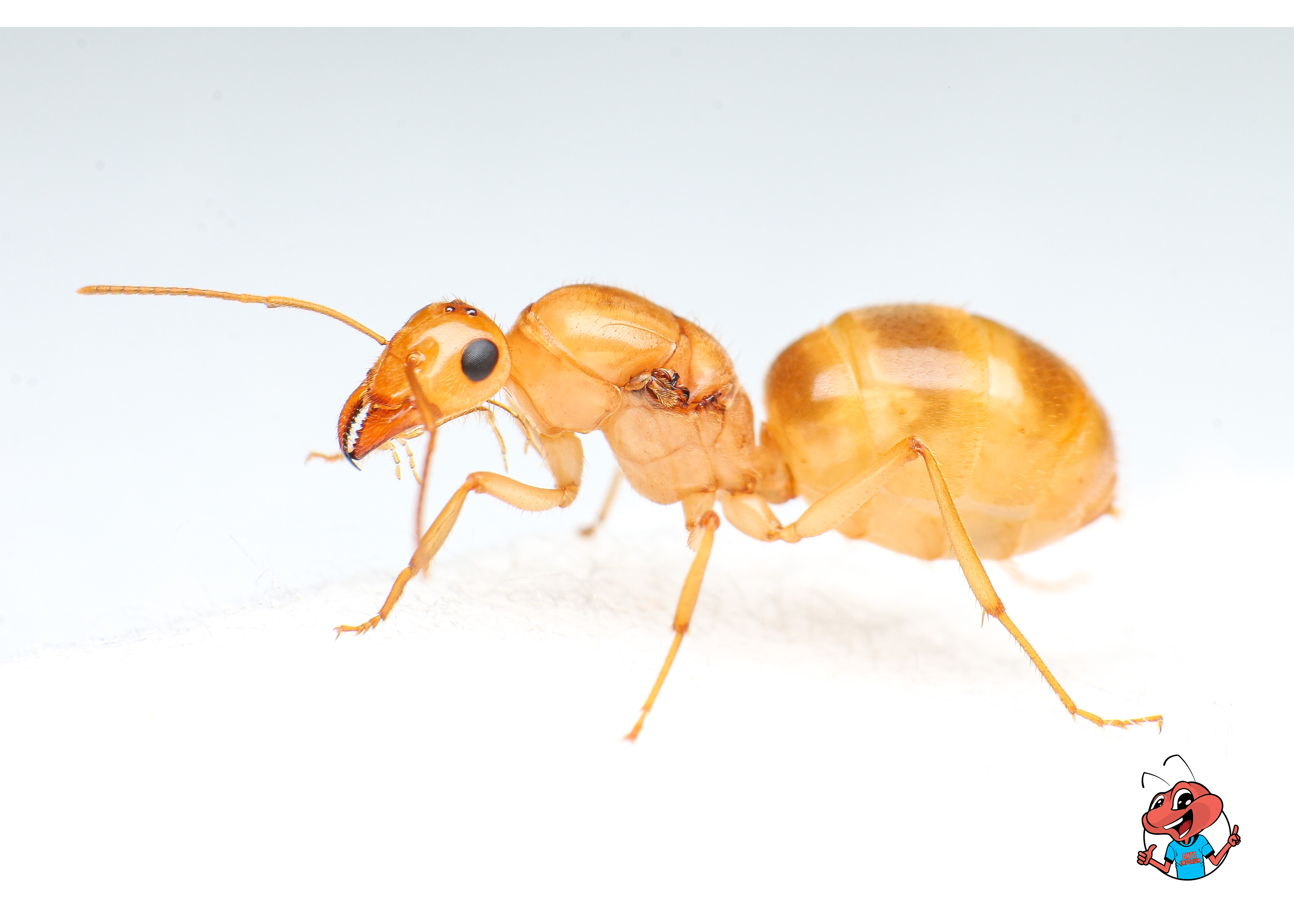
The development of an ant queen starts as a tiny egg, which hatches into a larva after a few days. The queen is then continuously fed by worker ants to support her growth, helping her to develop into a fully mature adult.
Once mature, the queen takes on the crucial role of reproduction, laying eggs that will hatch into worker ants and males. Queen ants have been known to lay thousands of eggs throughout their lifetime, demonstrating their remarkable reproductive abilities.
The queen's breeding abilities are essential for the survival and growth of the colony. Every worker ant in the colony is related to the queen, which strengthens the genetic makeup of the entire colony. Once the queen has successfully mated with a male ant from another colony, the colony begins to expand as the queen continues to lay eggs.
Another critical aspect of the queen's life is the construction and maintenance of the ant nest. The queen controls the construction of the nest and makes sure that it provides a suitable habitat for the colony to thrive. The ant nest is the central hub of the colony and serves as a place for food storage and a nursery for the queen's eggs.
As the queen ages, she may begin to experience a decline in egg production and reproductive abilities. This decline leads to the emergence of new queens that will replace the old queen. This process is known as colony succession and marks a new chapter in the life of the colony.
Overall, the life of an ant queen is full of challenges and responsibilities. Their unique role in the colony's social structure emphasizes the importance of the queen in maintaining the health and development of the colony.
Behaviors and Communication
Ant queens display a wide variety of behaviors that are specific to their role as the leaders and founders of ant colonies. These behaviors are necessary to maintain the cohesion and harmony of the colony, ensuring that everything runs smoothly.
One of the most important behaviors of ant queens is communication. Ants communicate primarily through pheromones, chemicals that they secrete and emit into the environment. Ant queens use these chemical signals to convey vital information to other ants, such as instructions on where to search for food or how to defend the colony.
Ants are also known to communicate through touch, with tactile cues such as antennation. In this behavior, ants touch each other with their antennae, transmitting information and communicating with one another.
Another important behavior of ant queens is their role in regulating the behavior of other ants within the colony. Ant queens are known to suppress the reproductive capabilities of other female ants, ensuring that they are the only ones responsible for breeding and producing offspring. This behavior is essential to maintain the social structure and ensure the survival of the colony.
Overall, the behaviors and communication methods of ant queens are critical to the success and efficiency of ant colonies. Their intimate knowledge of the colony and ability to communicate effectively with other ants ensure the smooth operation of the entire system.

Ant Queen Behaviors and Communication Table
| Behavior | Description |
|---|---|
| Pheromone Communication | Ant queens use chemicals to signal to other ants, conveying vital information and instructions for maintaining the colony. |
| Tactile Cues | Ants touch each other with their antennae to transmit information and communicate with one another. |
| Regulating Reproductive Capabilities | Ant queens actively suppress the reproductive capabilities of other female ants, ensuring that they are the sole breeders within the colony. |
The Social Structure of Ant Colonies
Ant colonies are some of the most well-organized societies in the animal kingdom. Their social structure is incredibly complex, and the role of the queen is of great importance. The queen ant is the founder of the colony and the only member capable of laying eggs, ensuring the continuation of the colony.
The hierarchy of ant colonies is structured around the queen, with worker ants providing support to their ruler. The workers are in charge of foraging, feeding the colony, and maintaining the nest. In return, they receive protection and care from their queen.
Ant colonies have several types of members, each with their own duties. The soldiers, for instance, play a crucial role in defending the colony from predators and enemies. They are larger and stronger than the other ants and have powerful mandibles that they can use to combat invaders.
"Ant colonies operate much like a well-oiled machine, with each member playing an essential role in the society's success. "
The social structure of ant colonies is maintained through complex communication. Ant queens are capable of emitting chemical signals, or pheromones, that allow them to communicate with their subjects. By doing so, they can regulate the behavior of the members, ensuring that the colony runs efficiently.
The social structure of ant colonies is a fascinating subject. Understanding the importance of ant queens in the colony's organization is vital in comprehending the inner workings of these complex societies.
Colony Founding and Succession
As we learned earlier, ant queens play a crucial role in establishing and maintaining ant colonies. Colony founding is the process by which ant queens initiate new colonies, ensuring the survival and expansion of their species. The colony's success depends on many factors, including the queen's lifespan, reproductive capacity and her ability to adapt to changes in the environment.
New colonies are founded in one of two ways. The first method involves the queen leaving her original colony and setting out on her own in search of a new location. Once she finds a suitable spot, she will lay the first eggs and start the foundation of her new colony. The other method is referred to as budding. When a colony reaches a certain size, the queen will produce new queens, and a portion of the population will split off to form a new colony.

When a queen's reign comes to an end, a succession process occurs. In some species, the old queen will produce a new queen before she dies, ensuring a smooth transition of power. Other species rely on competition between the female worker ants for the next queen.
The Importance of Colony Founding
Colony founding ensures the survival and expansion of the ant species by creating new colonies. When a colony grows too large, resources become scarce, leading to the establishment of new colonies, thus preventing overcrowding and ensuring the long-term sustainability of the species. Additionally, new colonies play a crucial role in expanding the ants' territory and searching for new sources of food, contributing to the growth and success of the entire species.
Challenges and Threats to Ant Queens
Ant queens are powerful leaders and the driving force behind ant colonies. However, even these remarkable insects face various challenges and threats throughout their lives. In this section, we will explore the dangers that ant queens encounter, including:
| Dangers | Description |
|---|---|
| Predators | Ant queens are preyed upon by many animals, including birds, lizards, and other insects. To protect themselves, they often remain in their nests and rely on their worker ants for protection. |
| Parasites | Ant queens can fall victim to parasites, such as mites and fungi, which can harm or even kill them. These parasites can spread rapidly throughout the colony if not managed effectively. |
| Environmental Factors | Ant queens must endure various environmental factors that can impact their survival, including extreme temperatures, droughts, and floods. They rely on their workers to maintain a suitable environment for the colony. |
Despite these challenges, ant queens are incredibly resilient creatures, and their ability to adapt and overcome adversity is a testament to their strength and leadership.
Through our exploration of ant queens and their role in ant colonies, we have gained new insights into the fascinating world of these insects. From their life cycle and behavior to their social structure and the challenges they face, ant queens truly are remarkable creatures that play a vital role in the insect kingdom.
Conclusion
We hope this article provided an insightful look into the fascinating world of ant queens and their role in the intricate ant social structure. As we have learned, queen ants are the founders and leaders of ant colonies, shaping the future of their kingdoms through their reproductive abilities and leadership.
Their influence on the hierarchy of ant colonies is paramount, and their succession is crucial to the survival and success of their colonies. However, we must also not forget the challenges and threats that ant queens face throughout their lives, including predators, parasites, and environmental factors.
In conclusion, ant queens are essential components of the ant social structure, and their contribution to maintaining the harmony and organization of ant colonies cannot be underestimated. We hope this article has further deepened your appreciation for these incredible insects.







Leave a comment